If you are reading the subject of biology, then you get to read about the cell in it. Today we will know about the Cell structure and cell cover of the cell through this post. If this topic is also related to your morning, then you must read the notes provided because you will probably not see such simple notes elsewhere, so you must not see anywhere else, so prepare them with notes for great preparation in a short time.
Cell structure and cell cover
Impportant facts
– In 1665 AD, ‘Robert Hooke’ first saw the cell, although Robert Hooke saw the dead cells, in which he saw the ‘cell wall’, still the credit for the discovery of the cell goes to Robert Hooke.
Note –
– Robert Hooke told about the cell in his book ‘Micrographia’.
– ‘Malpighi’ (in 1661 AD) observed cells before Robert Hooke and called them ‘Utriculli & Saccules’.
– During the year 1972-74, ‘Leuwinhoek’ saw the first living cell, he saw RBC, bacteria, sperm for the first time.
– In 1831, ‘Robert Brown’ first discovered the nucleus in the cells of the roots of orchid plants.
– In 1838, Schleiden and Schwann gave the cell theory, according to which –
– All organisms are made up of cells.
– These cells are the functional and structural units of the body.
– In 1855, ‘Rudolph Virchow’ was the first to say that new cells are formed from existing cells.
– Rudolf Virchow’s statement – Omnis Cellula e Cellula
Cell Structure
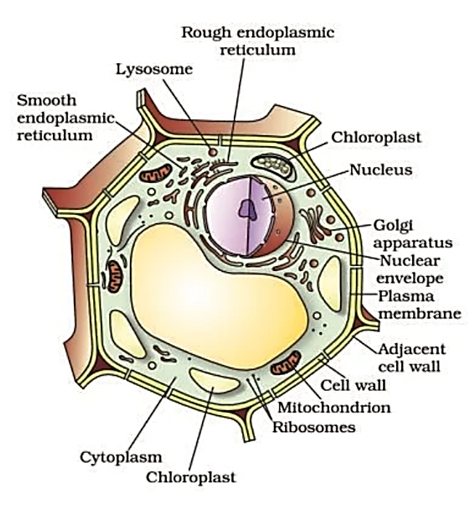
– Composition, On the basis of structure, cells are of two types-
(i) Prokaryotic/Asymmetric cell
(ii) Eukaryotic/Symmetric cell
| Prokaryotic / Asymmetric cell | Eukaryotic / Symmetric cell |
| – Nucleus is less developed and Nuclear membrane is absent around the nucleus. | – Nucleus is well developed and double nuclear membrane is found around the nucleus. |
| – DNA is in naked state. | – DNA consists of membrane. |
| – Circular DNA called plasmid and it is found outside the nucleoid (70’s ribosome). | – Spiral and double-stranded DNA are found inside the nucleus (80’s ribosome). |
| – There is no difference between Cytoplasm and Nucleoplasm. | – The cytoplasm and nucleoplasm are clearly differentiated from each other. |
| – Different types of cell organelles are not found. | – Well-developed cell organelles such as mitochondria, plastids,lysosomes, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum (E.R.), centrosomes, golgi bodies, etc are found. |
- Speedy Current Affairs November 2025 Pdf Free Download
- Africa Continent, Major Countries, Straits and Lakes
- Asia continent, Major countries, Jalasandhi and Lakes
- Vision Ias Today Current Affairs 10 May 2025
- Vision Ias Today Current Affairs 8 May 2025
Difference between Animal Cell and Plant Cell
| Plant Cell | Animal Cell |
| – The cell wall is mainly made of cellulose around the cell membrane. | – The cell wall is absent. |
| – Nucleus is comparatively small and towards the periphery. | – Nucleus is of large size and located in the center. |
| – Vacuoles are of large size. | – Vacuoles are small and scattered in the cytoplasm. |
| – Golgi bodies are underdeveloped and small in size called ‘dictyosomes’. | – Golgi bodies are well developed and large in size. |
| – Centrosome is absent. | – Centrosome is present. |
Cell Coat
Cell Wall
– It is the outermost covering of the cell which is found in Plant Cells, Fungi, Bacteria.
– Cell wall is absent in animal cells.
– It is secreted by the cell and is dead but metabolically active.
– Average thickness = 0.1 (micrometer) = 10-6 m
– The cell wall is made up of several layers/lamella.
Middle Lamella
– It is the cellular layer found between two cells.
– It is made up of pectate salts of calcium (Ca) and magnesium (Mg) which also act to hold two cells together. Hence it is also called ‘Cellular Cement’.
– During the ripening of fruits, salts start dissolving in water, due to which the fruits become soft.
Primary Lamella
– In plants, these cells are mainly composed of cellulose.
– Fungi are made from -14 acetyl glucosamine, also known as fungal cellulase. It shows similarity to chitin (the outer skeleton found on the body of insects).
– In bacteria, it is made from peptidoglycan.
– Pectin is found in the primary lamella. The protein ‘expansion’ is also found in this layer, due to which this primary wall has some expansion capability.
Secondary Lamella
– It is found on the inner side of the primary wall in mature cells.
– It is almost similar in structure to the primary wall.
– The deposition of certain substances is found in the secondary wall.
– Lignin – This makes the secondary wall hard and strong.
– Suberin – It is a wax-like substance, which controls the permeability of water.
– Cutin – This cutin forms the cuticle in plants, which regulates the process of transpiration.
Cell Membrane
– The cell membrane was discovered by ‘Schwan’.
– The name ‘Plasma Membrane’ was given by ‘Plow’ to the cell membrane.
– Nageli and Kramer called it the ‘cell membrane’.
– Cell membrane is found in all cells.
– Its average thickness is (Angstrom).
– It is semi permeable to water, selectively permeable to solutes.
– The cell membrane is mainly made up of fats (phospholipids) and proteins.
– To explain the structure of the cell membrane, Singar and Nicholson presented the Fluid Mosaic Model.
Note –
– Some pores are found in the cell wall, through these pores exchange of substances takes place between two adjacent cells. These structures are called plasmodesmata.
– Glyco Calyx – In some cells such as RBCs, gametes (sperm and egg) have an outer covering (made of carbohydrates)
Note : If you are preparing for UPSC, SSC or any other exam then definitely join us.

1 thought on “Cell structure and cell cover”