If you are studying the history of ancient India, then let us tell you that this post is for you only, in which you have been provided notes related to the Indus Valley Civilization, so to make your preparation great, definitely read these notes, you will not find such notes related to history anywhere else.
Indus Valley Civilization
– After the end of the Stone Age, the Age of Metals began. This era is called the Proto-historic period or the Metal period.
– Harappan culture is counted from this period.
– So far 4 civilizations of the world have come to light, which are respectively.
| Civilization Name | River |
| Mesopotamian | Tigris and Euphrates |
| Egyptian | Nile |
| India | Indus |
| Chinese | Huang-Ho (yellow river) |
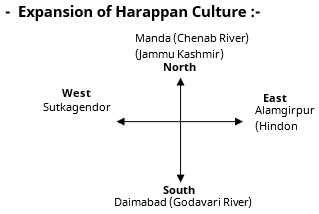
– The geographical extent of the Indus civilization was from Manda (Jammu) in the north to the mouth of the Narmada river in the south and from Sutkagendor in the west to Alamgirpur (Meerut) in the east.
– It extended from north to south about 1400 km and from east to west about 1600 km. So far, about 2800 sites have been discovered through excavation and research.
– At present, due to the new site coming to light, now its size is- Rhombus Quadrilateral (the original form was triangular)
– The Harappan civilization includes Punjab, Sindh, Baluchistan, Afghanistan, Gujarat, Rajasthan, Maharashtra, Haryana and ‘Parts of Western Uttar Pradesh’.
– John Marshall was the first archaeologist to use the name ‘Indus Civilization’.
– Amalanand Ghosh has considered the important contribution of ‘Sothi culture’ in the development of Harappa.
– In 1856, while laying the Karachi to Lahore railway line, for the first time some bricks were removed from the Harappan mound on the orders of James Burton and William Burton.
Major sites of Harappan Civilization
| Site | River | Excavators |
| Harappa | Ravi | Daya ram Sahani |
| Mohenjodaro | Indus | Rakhal Das Bannerji |
| Lothal | Bhogwa | S R Rao |
| Kalibangan | Ghaggar | Amalanand Gosh |
| Ropar | Sutlej | Y D Sharma |
| Kot Diji | Indus | Fazal Ahmed Khan |
| Chanhudaro | Indus | N G Majumdar |
| Rangpur | Bhadar | M S Vats |
| Alamgirpur | Hindon | Y D Sharma |
| Sutkagendor | Dasht | Aurel Stein |
| Banwali | Saraswati | Ravindra Singh Bisht |
– Radio Carbon Method:-
– On this basis the age of any object is determined.
– According to the radio carbon (C-14) date, Dr. DP Agrawal considered the Harappan civilization to be from 2300 BC to 1750 BC.
– Major places and features :-
Harappan
– According to Stuart Piggott, it was a semi-industrial city. A large part of the inhabitants here were engaged in trade, technical products and religious activities.
– It was discovered by Dayaram Sahni in the year 1921. Then the director of ASI was John Marshall. It is located in Montgomery (Pak, Punjab) presently Shahiwal.
Other remains found from Harappa:-
– A terracotta of a plant emerging from the womb of a woman has been found from Harappa, which is considered by the Harappans to be the goddess of fertility or the Earth goddess.
– A stone idol without a torso was found here.
– The city was spread over a area of about 5 km.
– To the south of the common housing area of Harappa, there is such a graveyard which has been named “Grave R-37”. Another grave – H has also been found.
– The mound on which the Harappan fort was located was named by Whiller as Mound-A-B.
– Bronze mirror
– The remains of two rows of granaries were found from Harappa, each containing 6-6 granaries.
– Cosmetic Box
– The most ornated seals – from Harappa, while the most – have been found from Mohenjodaro.
– The seals of the Indus civilization were made from the steatite.
– Evidence of labor accommodation has been found.
There were 3 types of seals ̵
1. Rectangular type
2. Circular type
3. Square type (most)
– The markings of a horned bull or deer, humpbacked bull, mother goddess, tiger, Pashupatinath and buffalo etc. are found on these seals.
Mohenjo-Daro :-

– Mohenjodaro was situated on the right bank of the river Indus, which is located (present-day) in Larkana district of Sindh province of Pakistan. It was discovered by Rakhaldas Banerjee in the year 1922. It is also known as the Oasis of Sindh.
– This city was ruined 8 times and settled 9 times, in which 7 successive levels have been found.
– The biggest building of Mohenjodaro was the granary, the Wheeler called it the granary and the largest public place was the ‘Great Bath’, this bath had religious significance. Big tanks have been found around it for water storage. John Marshall called it a wonderful creation of the then world, as well as called it a vast object.
– This is the most remarkable monument of Mohenjodaro.
– D D Kaushambi compares the Great Bath with the Pushkar and Kamalatal mentioned in the Sanskrit texts of the later period.
– A three-faced deity is depicted on a seal obtained from Mohenjodaro. Around which the marking of buffalo, elephant, rhinoceros, tiger and 2 deer on the lower part and fish and 10 letters on the upper part is found.
– John Marshall gave it the title of Pashupatinath, as well as gave it the likeness of ‘Proto Shiva’.
– Evidence of human skeleton (probably carnage) has been found from this site.
– Evidence of priestly residence has also been found from here.
– A bronze dancer’s idol has been obtained from here. It is made by liquid-wax method. The Harappans used to make bronze by mixing copper and tin.
– A seal obtained from Mohenjodaro depicts a yogi in a meditative posture with one leg on the other.
Lothal
– This is a place located in Gujarat. It was discovered in 1954-55 AD and its excavation was done by S-R Rao between 1957-58 AD.
– It was an industrial town.
– Beads making factory has been found from Lothal.
– There was a scale/ivory scale for weight-measurement.
– It was a major dock yard port of the Indus Civilization.
– Sikottri Mata was a sea goddess.
– Boat evidence suggests trade with Southeast Asian countries.
– This city is situated on the bank of Bhogwa river.
– The largest public place of the entire Indus civilization was the dockyard of Lothal. The evidence of the port has been received from here. Lothal was the main place of trade with West Asia at that time.
– Evidence of skull surgery has been found from here.
– There are three pairs of dead bodies (bodies buried together) whose head is towards the north and the feet are towards the south.
– Agnikund/Agnivedikas have been found from here.
– The most famous work of Lothal was the ship’s dockyard made of bricks, which was triangular. The most important of the seals found here are those found in the Gulf of Iran, which indicate trade relations with Mesopotamia and Persia (Iran).
– S R Rao called it Mini Harappa or Mini Mohenjodaro.
Kalibangan
– Along with the Harappan civilization, the remains of the pre-Harappan civilization have also been found from Kalibanga, that is, it is a pre-Harappan site.
– Kalibanga is situated on the left bank of Ghaggar river in Hanumangarh district of Rajasthan.
– Literal meaning of Kalibangan is black bangle.
– Kalibanga was discovered by Amalanand Ghosh in 1952-53 AD and excavation was done between 1961-67 AD.
Evidence found from Kalibangan –
First evidence of camel
Evidence of plow shape and plowed field has been found.
The people of Kalibanga used to sow two crops simultaneously.
It was known as ‘Deen-Heen’ soceity.
Evidence of wooden drains
Evidence of skull surgery
A skull obtained from here has been found with piercings, which is considered to be the proof of surgery.
– Evidence of three types of burial has been found from Kalibanga.
Complete Burial
Fractional Burial
Post Cremation Burial
– Evidence of the world’s first earthquake was found from Kalibanga, which was around 2100 BC.
– Evidence of ornate floors, brick and cylindrical pieces and Havan Kund.
Chanhudaro :-
Chanhudaro is located 130 km south of Mohenjodaro. It was first discovered in 1930-31 by Nani Gopal Majumdar (NG Majumdar). The excavation was done in the year 1935 by Ernest MacKey.
Chanhudaro is the only site of the Indus Valley Civilization, from where curved bricks have been found.
From here :-
– Evidence of a bead-making factory
– Remnants of cosmetics (eg- lipstick) have been found here.
– Elephant toy
– Brass horse carriage
– Evidence of ink pot has been found.
Banwali :-
– Banwali is situated on the banks of Saraswati river in Hisar district of Haryana.
– It was discovered in 1974 by R.S. Bisht.
– From here clay toys (plough) have been obtained.
Rangpur :-
– Rangpur is located near the Bhadar river in the Kathiawar peninsula of Gujarat.
– It was discovered by S R Rao in 1974.
Surkotada :
– This site was discovered by Jagpati Joshi in 1964 in the Kutch region of Gujarat state.
– Remains of horse bone have been found from here.
– Evidence of Kalash burial has been found from here.
Dholavira
– It is located in Bhachau Taluka of Kutch District of Gujarat State. It is located in Dholavira.
– It was discovered in the year 1967-68 by J P Joshi and excavated by R S Bisht in the year 1991.
– The only stadium (playground) of the Indus Valley Civilization has been found from here.
– Remains of horse artifacts have also been found.
– Unlike other Harappan sites, the city of Dholavira is divided into three sections, that is, the remains of “Madhyama” have been found only from this site–
1. Citade
2. The Middle town
3. The Lower town
Sutkagendor :-
– Sutkagendor is located on the Dashak River in the Balochistan province of Pakistan. It is the westernmost known city of the Indus Valley Civilization.
– From here the existence of the port is known.
Alamgirpur :-
– Alamgirpur is situated on the banks of Hindon river in Meerut district of Uttar Pradesh state.
– Not a single Idol of Mother Goddess and currency has been received from here.
– The ‘Bharat Sevak Samaj’ organization had a special contribution in the discovery of this site and the excavation was done by Yagyadat Sharma in 1958.
Ropar :-
– It was discovered by B B Lal in 1950.
– In 1953-56 AD Yagyadutt Sharma got the excavation done.
– The remains of pre-Harappan and Harappan cultures have been found here.
Rakhigarhi :-
– This site was discovered by Rafiq Mughal and Surajbhan.
– This site is situated on the Ghaggar river in Jind district of Haryana state.
– Rakhigarhi is one of the largest cities of Harappan civilization located in India.
Social Life:-
– The people of this civilization used to eat wheat, barley, dates and meat in their food.
– Indus society was divided into four classes-
(1) Scholar (Purohit)
(2) Warrior
(3) Merchant
(4) Labor
– Both cotton and woolen clothes were used.
– Fishing, hunting, chappar, playing dice were the means of entertainment.
– Dice was the main game of this era.
– The unit of society was traditionally the family.
– The people of the Indus Valley Civilization also paid attention to the decoration. Jewelery of both men and women has been found in the excavation.
Religious Belief :-
Evidence of Swastika has been received from this civilization.
The remains of the temple have not been found from anywhere in this civilization.
There is ample evidence of linga worship which has been later associated with Shiva. Several yoni figures of stone have also been found, which were worshiped as fertility.
Political situation :-
– The Harappan civilization was based on trade and commerce. Therefore, the merchant class also had an important role in the governance system.
– According to scholars like Piggatt and Wheeler etc., like Sumer and Akkad, the priestly people ruled in Mohenjodaro and Harappa too. These governments took full care of the interest of the people. Probably Mohenjodaro and Harappa were the two capitals of his kingdom.
Economic life:
– It has been inferred from the archaeological evidence that the people of Indus civilization did not cultivate with plow or spade. It is possible that these people cultivated the land by digging the land with stone axes or with wooden plows. The tools of these people were very crude, but the farmers here used to grow more food than they needed. The surplus grain was used for trade and commerce.
– The people of Indus Valley knew many industries apart from agriculture. These people knew well how to grow and spin cotton. It is possible that cotton and cotton cloth were exported. They made various types of pottery and dyed clothes.
Agriculture :
– The main crops of the Harappan culture were wheat and barley. Apart from this, they also produced rye, peas, sesame, gram, cotton, dates, watermelon etc.
Evidence of rice production has been received from Lothal and Rangpur.
Evidence of irrigation from canals and drains has not been found from any site.
Animal Husbandry:
– The main animals domesticated in the Harappan civilization were bulls, sheep, deer, peacocks, cows, mules, goats, buffaloes, pigs, elephants, dogs, donkeys etc.
– The humpback bull was especially dear to the Harappans.
– Camel, rhinoceros, fish, turtle are depicted on the coins of Harappan culture.
– Metal workers used to prepare bronze by mixing tin with copper.
– A piece of cotton cloth made from Mohenjodaro and the impression of cotton cloth on an clay pot at Kalibanga has been found.
– The people of this civilization did not know about iron.
– Bronze idol is made by Dravi-wax method.
Art :
The people of Indus Valley had made a lot of progress in the field of art. They used to make beautiful pictures on utensils. Pictures of humans and animals are found in large numbers. The artistic interest of these people is revealed from the pictures of animals made on the seals. These pictures are of animals like bull, elephant, cheetah, reindeer, gharial, rhinoceros etc.
Business :
The Harappans used to trade with Rajasthan,Saurashtra,Maharashtr,South India and Bihar.
They had trade links with Mesopotamia, Sumer and Bahrain.
Mesopotamian inscriptions of 2350 BC mention trade relations with Meluha (ancient part of Sindh region).
Measurements:
An oyster scale has been found from Mohenjodaro and an ivory scale from Lothal.
A series of weighing systems dealt with 1, 2, 4, 8 to 64, and 16 or its repeaters, such as -16, 64, 160, 320 and 640.
Seal and Script:
Maximum number of seals have been received from Mohenjodaro.
Most of the seals received are made of steatite.
The largest figure of a horned animal has been found on the seals. Copper seals have been found from Lothal and Desalpur.
The Harappan script is not descriptive, but mainly pictorial.
A picture of a boat has also been found on each seal of Lothal and Mohenjodaro.
The shape of the seals was circular, oval, cuboidal and rectangular, square and square seals have also been found.
The first samples of the script were obtained by Cunningham in 1853 AD.
Its other names are :-
– Spirala Script
– Gaumutri Script
– Boustrophedosquaren /Phedas / Phedum (pictographic Sript)
The first attempt to read the script of the Indus Valley Civilization was made by ‘Weiden sir’. Natwar Jha was the first Indian to try to read this script, but failed to read it.
– The knowledge of Saindhav script is mainly found on seals.
– There are 64 basic symbols in this script while there are 250-400 pictographs.
– Most of the pictographs are in the shape of an inverted ‘∩’
If you are preparing for UPSC, SSC or any other exam then definitely join us.

2 thoughts on “Indus Valley Civilization Notes Upsc”