If you are studying the history of ancient India, then let us tell you that this post is for you only, in which you have been provided notes related to the Stone Age, so to make your preparation great, definitely read these notes.
Stone Age
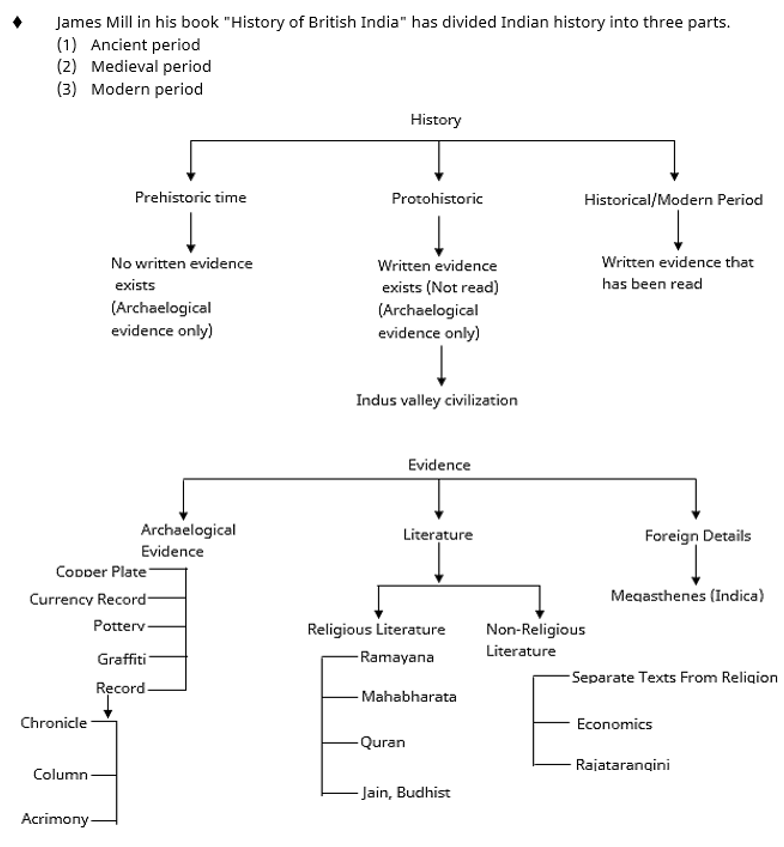
– The Stone Age is divided into three parts-
(1) Palaeolithic period
(2) Mesolithic period
(3) Neolithic period
1. Palaeolithic Period
– This is the time of the prehistoric era when humans first started making stone tools.
– In this era the earth was covered with snow. The Indian Palaeolithic is divided into three parts on the basis of the nature of stone tools used by humans and the change in climate-
(i) Lower Palaeolithic : (between 500000 BC to 50000 BC)
(ii) Middle Palaeolithic : (between 50000 BC to 40000 BC)
(iii) Upper Palaeolithic : (between 40000 BC to 10000 BC)
– In India, the remains of Palaeolithic period have been found from Kurnool in Andhra Pradesh, Husgi in Karnataka, Kuliana in Odisha and Didwana in Rajasthan and Bhimbetka in Madhya Pradesh.
2. Mesolithic Period
– It is the transition period between the Palaeolithic and the Neolithic. Its time period is considered from 9000 BC. to 4000 BC. There were very small stone tools in this period. In the Mesolithic period, there were many fine-stone tools such as the major tool plank, point, khurchan, vedhni.
– The earliest evidence of animal husbandry is also found in this period.
– The earliest evidence of animal husbandry has been found from Adamgarh in Madhya Pradesh and Bagor in Rajasthan during this period.
– The following are the major Mesolithic areas – Sambhar Lake, Langnaj, Sarai Nahar, Mahadaha, Bhimbetka, Virbhanpur etc.
3. Neolithic Period
– Man invented fire (use of fire in normal life like – cooking food, clearing forest etc.).
– Evidence of permanent settlement is found from – Mehrangarh (Pakistan). Evidence of farming or agriculture has been found in this age.
– Invention of wheel – Considered to be the most revolutionary invention of this period.
– The primitive man first invented copper as a metal.
– He made pottery for storing grain.
– Humans made rapid progress in the Neolithic period. Although the weapons of man were made of stone in this period, but they were sharpened and polished and made shiny, in this period man had made more progress than other times.
– During this period, man started growing food by farming, so now he started using everything for food to fulfill his stomach. With the help of fire, he started cooking his food. Many utensils for cooking food have been found in the excavation.
– The Neolithic culture was more developed than its predecessors Culture. The man of this period was not only a consumer of food, but he was also a producer. He had become fully acquainted with agriculture and animal husbandry.
Protohistory
– After the end of the Stone Age, the Age of Metals began. This era is called the Proto-historic period or the Metal period.
– Harappan culture and Vedic culture are counted from this period.
– So far 4 civilizations of the world have come to light, which are respectively.
| Civilization Name | River |
| Mesopotamian | Tigris and Euphrates |
| Egyptian | Nile |
| India | Indus |
| Chinese | Huang-He (yellow river) |
| Classification of Period | Indian type of tools | Lifestyle | Key points | |
| Paleolithic Age | Lower Paleolithic Age | Cores, tools such as hand axe cleavers and chopping toolsTools – scales, gandasa, khandaka, hand axe and batikasham. | hunting and gathering | Stone tools were found in Sohan river valley (Punjab province of Pakistan), Singrauli valley (UP), Chota Nagpur, Narmada valley and all India except Sindh and Kerala. |
| Middle Paleolithic Age | flake tool (Tools made by Core made from Levallois Technique)Tools – Borers, scrapper and Points. | hunting and gathering | Nevasa (Maharashtra), Didwana (Rajasthan), Bhimbetka, Narmada Valley (Madhya Pradesh), Purulia (West Bengal), Tungabhadra River Valley and all of India Sindh (Pakistan), all over India except Kerala. | |
| Upper Paleolithic Age | Flake blades such as parallel plank blades and burinTools- chisel, blade, scrapper, harpoon, pure blade industry have been found from Belan valley, huge collection of blades and knives from Renigunta and bone tools have been found from Kurnool. | hunting and gathering | Reniguntu Tada Kurnool (Andhra Pradesh), Sholapur, Bijapur, Belan Valley | |
| Mesolithic Age | Microlith or MicrotoolTools – Tools made of microliths – blades, crescent shaped tools, single edged tools, triangles, demilune and trapezoidal tools, pointed tools. | Hunting, gathering, fishing and animal husbandry | Areas of Bagor, Panchpadra Valley and Sojat (Rajasthan), Langhnaj (Gujarat), Akkhaj, Balsana, Vindhya and Satpura, and Bhimbetka (Madhya Pradesh), Adamgarh (Bihar), Virbhanpur (West Bengal), Sangankal (Karnataka), Sarainahar Rai , Lekhhima, Morhana mountain (UP) | |
| New Stone Age/Neolithic Age | Celt glazed hand axes and whole axesMain tools-polished stone tools, stone axes, small stone tools and bone tools | Food production based on animal husbandry and agriculture | Adamgarh and Chirand (Bihar), Baluchistan, Belan Valley of Uttar Pradesh, Burzahom and Guffarkaral (Jammu and Kashmir), Mehrgarh, Peninsular India, Kotdiji. | |
If you are preparing for UPSC, SSC or any other exam then definitely join us.

1 thought on “Stone Age ( Ancient History ) Notes in English”